With the rapid development of new energy vehicles, intelligence, lightweighting and integration will be the trends in the development of electric vehicles. The OBC directly determines the safety and stability of new energy vehicles. Its power density directly affects the quality, range and charging time of the entire vehicle.
Silicon carbide, as the third-generation semiconductor, has excellent properties such as high temperature resistance, high voltage resistance, high frequency and radiation resistance. SiC MOSFET can reduce the power conversion energy loss of the vehicle by 20%, playing an important role in improving the efficiency, power density and quality density of OBC products.
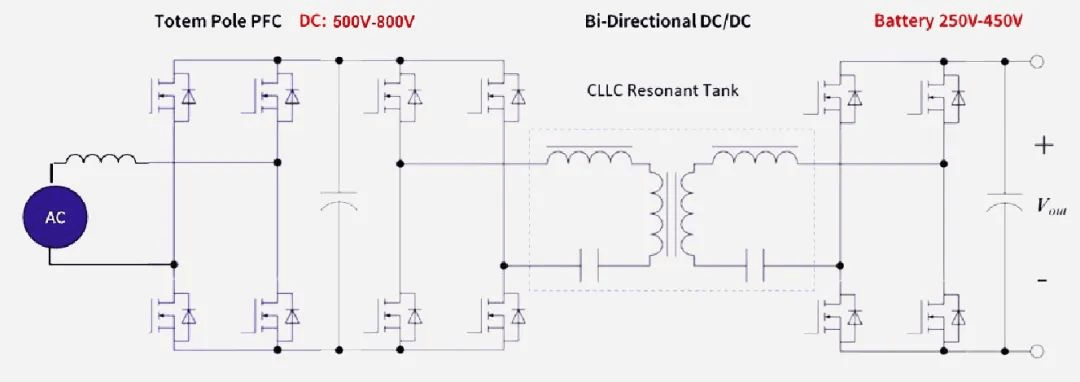
The working principle of the bidirectional vehicle charger (OBC) involves two core functions: charging the electric vehicle from the power grid (AC to DC), and reversing the flow of electricity from the vehicle back to the power grid or other systems (DC to AC).
Charging the vehicle from the power grid (AC to DC)
- Receiving alternating current (AC): When the vehicle is connected to an alternating current power source, such as a household power source or a public charging station, the bidirectional OBC receives alternating current.
- AC-DC conversion: After the alternating current enters the OBC, it passes through an AC-DC converter. This converter is usually equipped with a rectifier, which can convert alternating current to direct current.
- Battery charging: The converted direct current is then used to charge the vehicle's battery.
Reversing the flow of electricity from the vehicle back to the power grid (DC to AC)
- Using direct current (DC): In the reverse mode, the OBC uses the direct current stored in the vehicle's battery.
- DC-AC conversion: This direct current is sent to a DC-AC inverter, which converts the direct current to alternating current.
- Feedback to the power grid or household power supply: The converted alternating current can be sent back to the power grid or used for various applications in households or office facilities, such as providing power to the power grid during peak hours or supplying power when there is a sudden increase in electricity demand in the household.
The following is the application topology diagram:
Totem Pole PFC:
The Totem Pole PFC is a highly efficient power factor correction (PFC) technology used in power electronics. Power factor correction is a method to enhance the efficiency of the power system by reducing the generation of reactive power, thereby improving the utilization efficiency of electrical energy.
Compared with traditional PFC circuits, the main features of the Totem Pole PFC are high efficiency, low harmonic distortion, simplified circuit design, suitability for high-power applications, compatibility with new semiconductor technologies, and is particularly suitable for modern power supply solutions that require high performance and energy conservation.
Bi-Directional DC/DC
Bidirectional DC/DC Converter: It is a power conversion device that can achieve bidirectional energy conversion between two DC voltage levels. This means it can switch between boost (upward voltage) and buck (downward voltage) modes.
Bidirectional DC/DC converters are applied in fields such as electric vehicles (EVs), renewable energy systems, energy storage systems, and industrial applications. By providing flexible power management, bidirectional DC/DC converters offer crucial technical support for energy efficiency and smart grid integration.
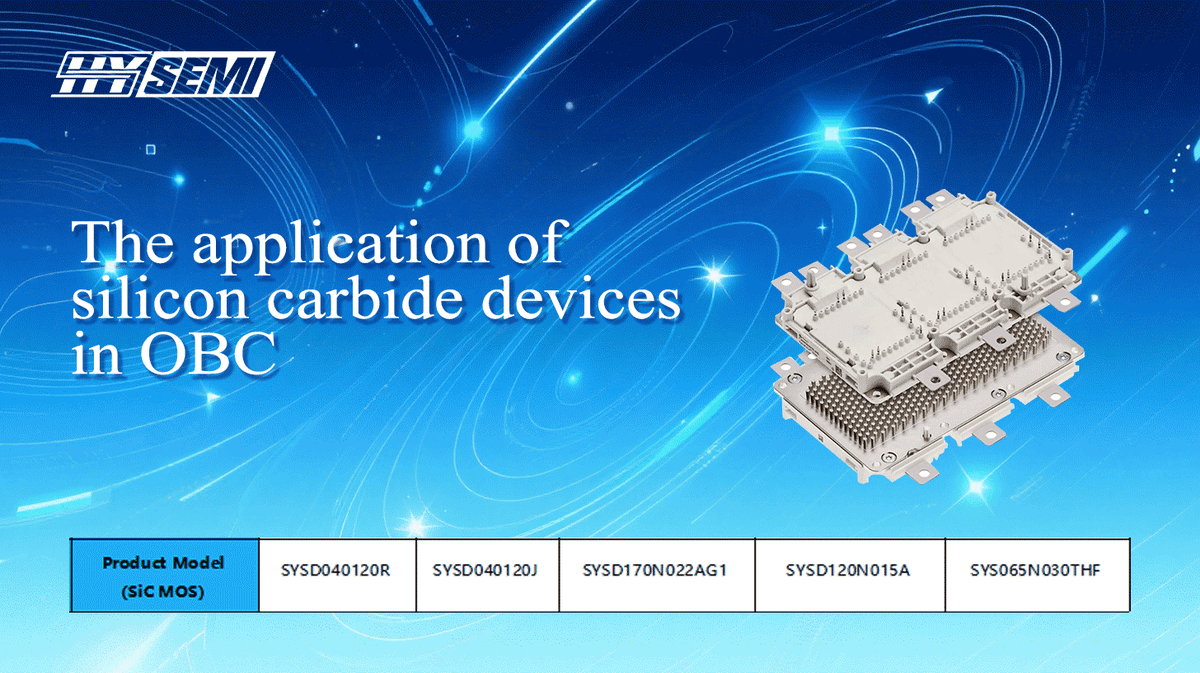
Here are the main product recommendations from SHYSEMI in the OBC application field:

The application advantages of silicon carbide two-terminal devices in bidirectional OBC
- High performance: Low switching/conduction losses, improving power conversion efficiency, especially suitable for high-frequency applications.
- Energy saving and heat dissipation optimization: Excellent high-temperature performance, reducing cooling requirements; efficient conversion reduces energy loss.
- High reliability: Resistant to high temperatures and high voltages, enhancing system stability and lifespan.
- Compact design: Supports high-frequency operation, realizes miniaturization of components, reduces system volume/weight, and facilitates integration.
- Comprehensive performance: High efficiency, high-frequency operation, high-temperature stability, and long-term durability, reducing overall costs.