The Power Control Revolution
High-power electronics demand efficient, reliable switching. This is where the insulated gate bipolar transistor (IGBT) shines. Combining MOSFET and BJT advantages, it dominates industries from energy grids to electric vehicles.
What makes insulated gate bipolar transistor tech superior? Three key factors:
✔ High voltage handling
✔ Low conduction losses
✔ Robust thermal performance
How Insulated Gate Bipolar Transistor Works
1. Structure & Operation
The insulated gate controls current flow between collector and emitter. Unlike MOSFETs, IGBTs add a bipolar junction for better conductivity.
Key components:
- Insulated gate (voltage-controlled)
- P+ substrate (enables high current)
- N- drift layer (blocks high voltage)
2. Switching Mechanism
- Gate voltage creates/destroys conduction channel
- Faster turn-off than BJTs
- Handles high power IGBT demands effortlessly
Why IGBTs Beat Alternatives
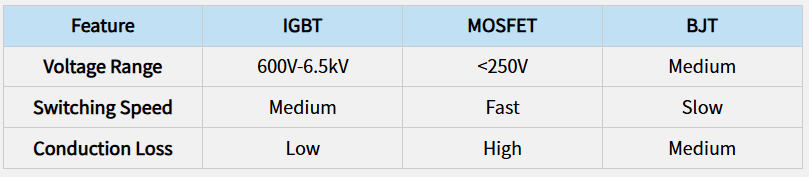
1. High Voltage Edge
High voltage IGBT modules excel in:
- HVDC power transmission
- Industrial motor drives
- Railway traction systems
2. Thermal Advantages
- Handles 150°C+ continuously
- Integrates with liquid cooling
3. Cost Efficiency
- Lower system costs vs. SiC alternatives
- Proven reliability
Key Applications
1. Energy Infrastructure
- IGBT power converters in smart grids
- Wind turbine generators
- Traction inverters
- Fast-charging stations
- Welding machines
- Induction heating
Future Innovations
1. SiC-IGBT hybrids for higher efficiency
2. Smarter modules with embedded sensors
3. Lower-cost packaging for mass adoption
Conclusion
The insulated gate bipolar transistor remains unmatched for:
✔ Heavy industrial systems
✔ Energy infrastructure
✔ Transportation electrification
As power demands grow, IGBT tech continues evolving.